
Destinations
Creating Destinations
This section will help guide you to create a destination to store your backups. To create a destination, click on “Create New Destination”
Destination Types
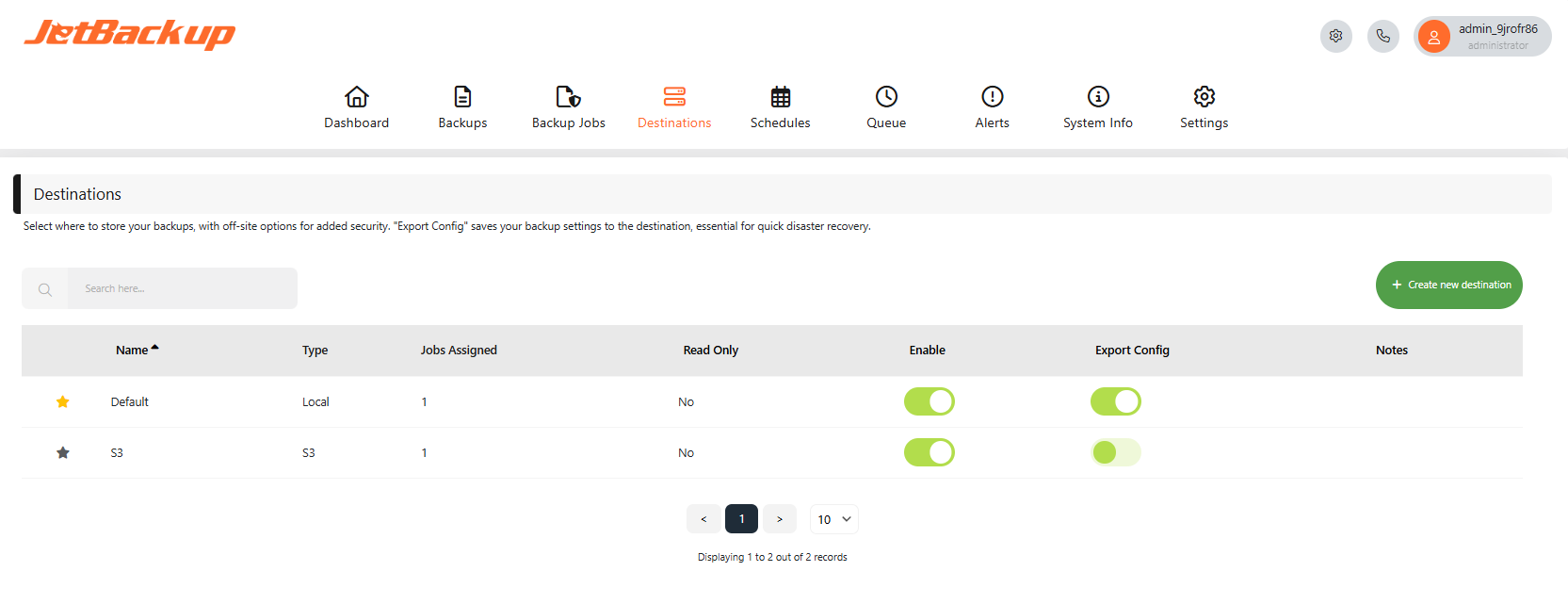
Local Destination Example:
Default Destination
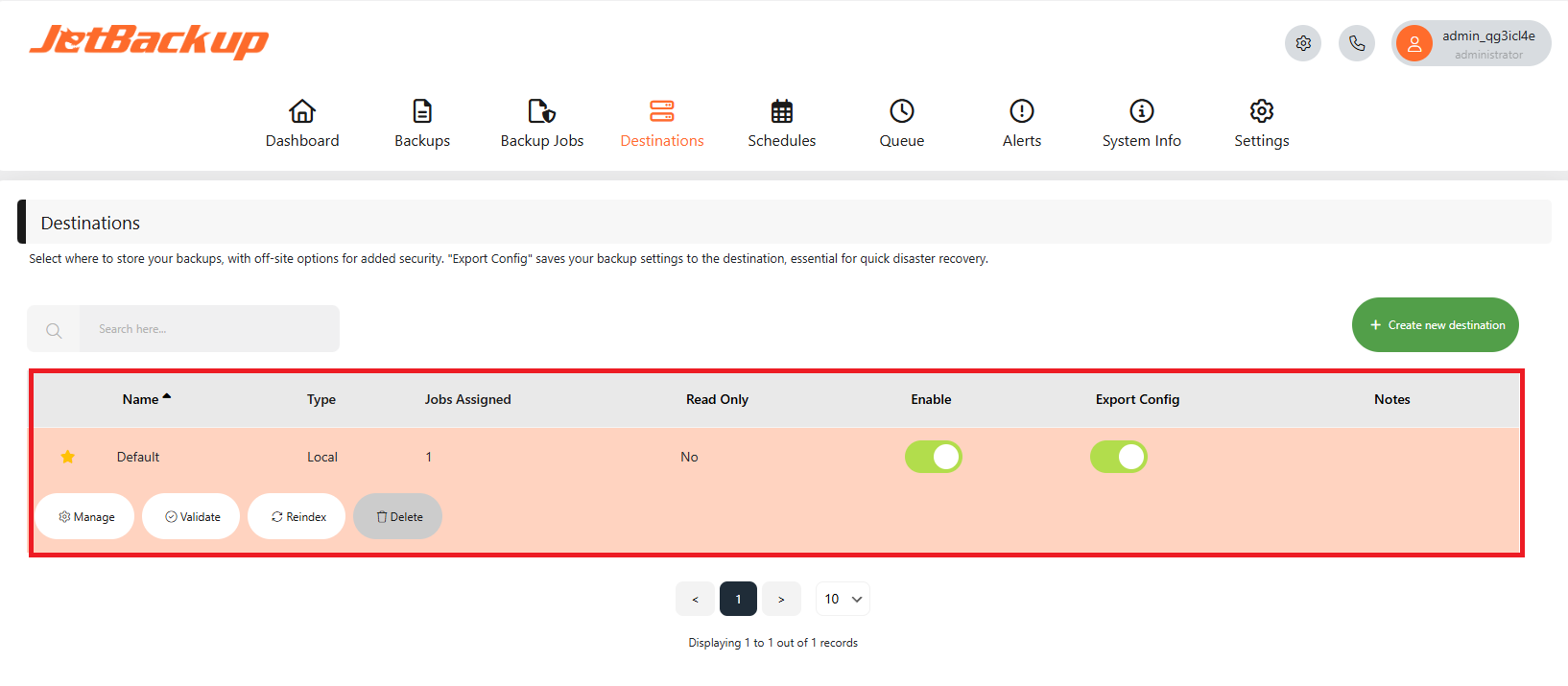
When JetBackup for WordPress is first opened, a Default Destination (Local) is already configured. The Backup Directory for this destination is set to transfer backups to the JetBackup Data Directory. You may find the configuration to this destination below:
Default Destination Configurations
Name: Default
Chunk Size: 1MB
Free Disk limit: Disabled
Backup Directory: /
Please note that the Default Destination can be modified, however, it cannot be deleted.
Name
Specify a name for the destination.
Notes
Enter notes for the destination.
Read Only
This option allows users to add destinations as a “Read-Only” destination. This type of destination will only be able to restore and download existing backups.
Chunk Size
Adjust the default read/write chunk size. Smaller chunks are ideal for small files or slow connections, while larger chunks work best for big files on fast, stable networks.
Free Disk Limit
This option prevents backups if the destination disk space reaches the specified limit. If this option is enabled and the available disk space is less than the amount specified, the backup job will not execute.
Backup Directory
Specify the directory on the remote server where backups will be stored.
Export Config
This option stores your backup settings to the destination, ensuring a fast recovery in case of a disaster.
Supported Cloud Destinations
A Cloud destination serves as a remote storage location for your backup files. Below is a list and brief overview of each supported cloud destination types so you can choose the most suitable destination for your specific needs or use case.
In general, it is almost always a best practice to make sure at least one copy of your server’s backups are located off-site (remote destination) in case of a disaster at your data center, home, or office happens.
Remote destinations are usually slower than local destinations to backup and restore from due to your network’s available bandwidth, distance between where your website is hosted and where your cloud storage is located, etc. With this in consideration, many clients choose to store at least one copy of backups locally and additional copies in at least one or more remote destinations.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.